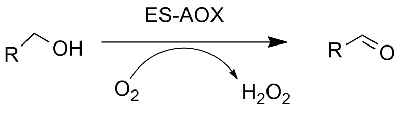
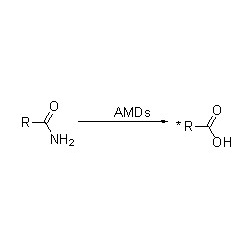
Alcohol oxidase (AOX)
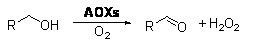
| Enzymes | Product Code | Specification |
| Enzyme Powder | ES-AOX-101~ ES-AOX-105 | a set of 5 alcohol oxidases, 50 mg each 5 items * 50mg / item, or other quantity |
| Screening Kit (SynKit) | ES-AOX-500 | a set of 5 alcohol oxidases, 50 mg each 5 items * 50mg / item, or other quantity |
★ High substrate specificity.
★ High conversion.
★ Less by-products.
★ Mild reaction conditions.
★ Environmentally friendly.
➢ Normally, the reaction system should include substrate, buffer solution and ES-AOX, and oxygen should be present.
➢ All kinds of ES-AOXs corresponding to various optimum reaction conditions, which could be studied individually.
➢ High concentration Substrate or product with may inhibit ES-AOX's activity. However, the inhibition can be relieved by batch addition of substrate.
➢ The accumulation of H2O2 in the system will lead to enzyme inactivation, which can be effectively solved by the use of catalase.
Example 1(Oxidation of aryl-alcohols) (1):
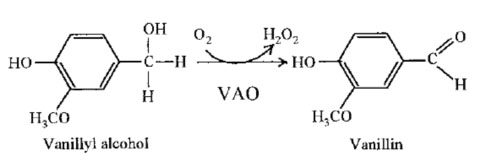
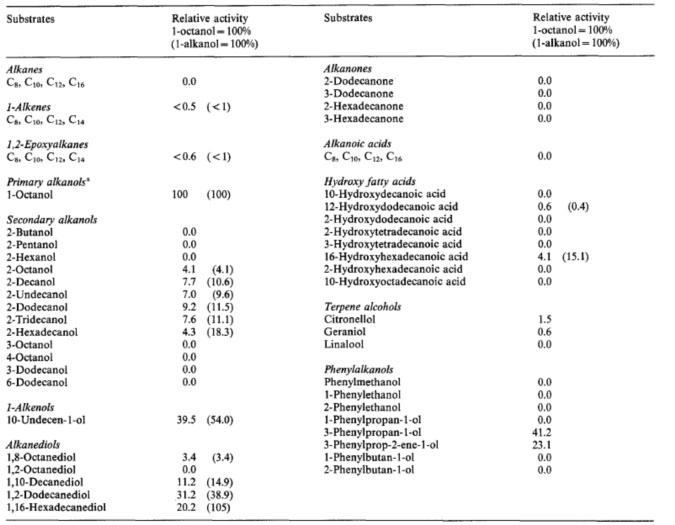
Example 2(Oxidation of fatty alcohols) (2):
Keep 2 years below -20℃.
Never contact with extreme conditions such as: high temperature, high/low pH and high concentration organic solvent.
1. Benen J A. E., Sa' nchez-Torres P, Wagemaker M J. M., e tal. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273(14): 7865-7872.
2. Mauersberger S, Drechsler H, Oehme G, e tal. Appl Microbiol Biot, 1992, 37: 66-73.