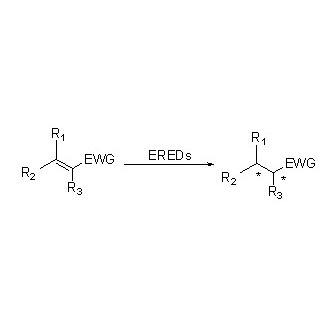
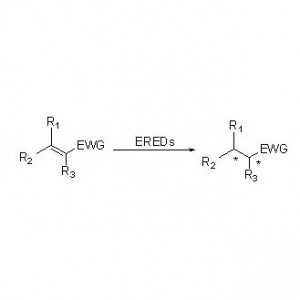
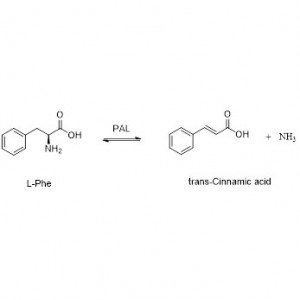
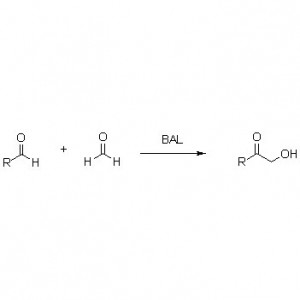
Ene reductase (ERED)
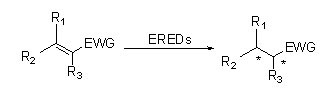
ES-EREDs catalyze various substrate types because of wide spectrum of substrates. In general, the C=C of α, β -unsaturated compounds with electron-absorbing groups (including ketone aldehyde, nitro groups, carboxylic acids, esters, anhydride, lactones, imines, etc.) are easily reduced by ES-EREDs, but the unactivated double bonds not.
There are 46 kinds of ERED enzyme products (Number as ES-ERED-101~ES-ERED-146) developed by SyncoZymes.
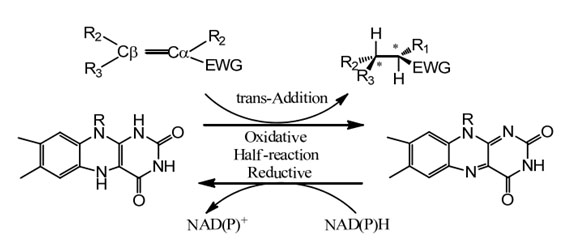
Catalytic mechanism:
| Enzymes | Product Code | Specification |
| Enzyme Powder | ES-ERED-101~ ES-ERED-146 | a set of 46 Ene Reductases, 50 mg each 46 items * 50mg / item, or other quantity |
| Screening Kit (SynKit) | ES-ERED-4600 | a set of 46 Ene Reductases, 50 mg each 46 items * 50mg / item, or other quantity |
★ High substrate specificity.
★ Strong chiral selectivity.
★ High conversion.
★ Less by-products.
★ Mild reaction conditions.
★ Environmentally friendly.
★ High safety.
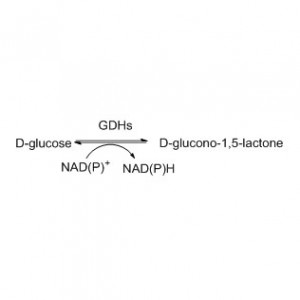
➢ Normally, the reaction system should include substrate, buffer solution (optimum reaction pH), coenzymes(NAD(H) or NADP(H) ), coenzyme regeneration system(e.g. glucose and glucose dehydrogenase) and ES-ERED.
➢ All the ES-EREDs can be tested respectively in the reaction system above or with the ERED Screening Kit (SynKit ERED).
➢ All kinds of ES-EREDs corresponding to various optimum reaction conditions should be studied individually.
➢ High concentration Substrate or product with may inhibit ES-ERED’s activity. However, the inhibition can be relieved by batch addition of substrate.
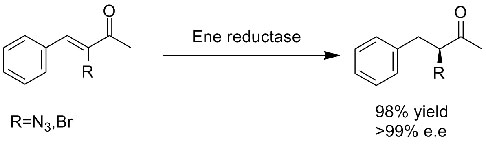
Example 1(α,β-unsaturated aldehydes or ketones) (1):
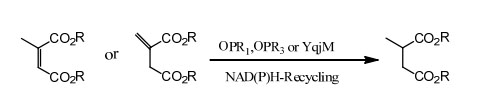
Example 2(α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids and their derivatives) (2):
Keep 2 years below -20℃.
Never contact with extreme conditions such as: high temperature, high/low pH and high concentration organic solvent.
1. Lucídio C, Fardelone J, Augusto R, e tal. J.Mol.Catal.B:Enzym., 2004, 29: 41-45.
2. Stueckler C, Hall M, Ehammer H, e tal. .Org.Lett, 2007, 9(26): 5409-5411.